Services
Hand & Upper Extremity Rehabilitation
Hand Therapy is a type of rehabilitation performed by an occupational or physical therapist on patients with conditions affecting the hands and upper extremities. Such therapy is performed by a provider with a high degree of specialization that requires continuing education and, often, advanced certification. This enables the hand therapist to work with patients to hasten their return to a productive lifestyle.
A hand therapist works with clients having a variety of upper extremity disorders. A hand therapist may serve clients who have been affected by an accident or trauma leaving them with scars, burns, injured tendons or nerves, fractures, or amputations of the finger, hand, or arm. Hand therapists also treat clients who are disabled from the effects of repetitive strain injuries (RSI) such as tennis elbow and carpal tunnel syndrome.
Who is a Certified Hand Therapist?
A Certified Hand Therapist (CHT) is an occupational therapist or physical therapist who has a minimum of three years of clinical experience, including 4,000 hours or more in direct practice in hand therapy. In addition, the Certified Hand Therapist has successfully passed a comprehensive test of advanced clinical skills and theory in upper quarter rehabilitation. Because of changes in the profession, every CHT is required to demonstrate continued professional development and competency by recertifying every five years.
Hand Rehabilitation Services
Comprehensive initial evaluation
Provision of an individualized treatment plan
Client education
Manual hands-on treatment
Active and passive range of motion exercises
Strengthening exercises
Management of scars
Management of swelling
Desensitization
Dry needling
Home exercise programs
Provision of custom or prefabricated splints/braces
Application of physical & electrophysical modalities:
- Whirlpool
- Heat Packs
- Paraffin Wax Bath
- Application of Cold
- Ultrasound
- Neuromuscular Electrical Stimulation (NMES)
- Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation (TENS)
- Instrument Assisted Soft Tissue Mobilization (IASTM)
- Pulsed Radiofrequency (Stimpod 460)
- Low Level Laser Therapy (LLLT)
- Radial Shockwave Therapy

Conditions Treated
Traumatic Injuries
- Crush Injuries
- Dislocations
- Fractures
- Tendon/Nerve Injuries
- Sprains and Strains
RSI & Systemic Conditions
- Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
- deQuervain’s Tenosynovitis
- Lateral/ Medial Epicondylitis
- Tendonitis/Tenosynovitis
- Trigger Finger/Thumb
- Arthritis (RA/OA)
Post-surgical Conditions
- Amputations
- Carpal Tunnel Release
- Dupuytren’s Release
- Fracture Fixation
- Ganglionectomy
- Joint Replacements and Reconstructions
- Nerve Repairs
- Tendon Repairs
- Tenolysis
- Trigger Finger/Thumb Release
- Wrist Surgery
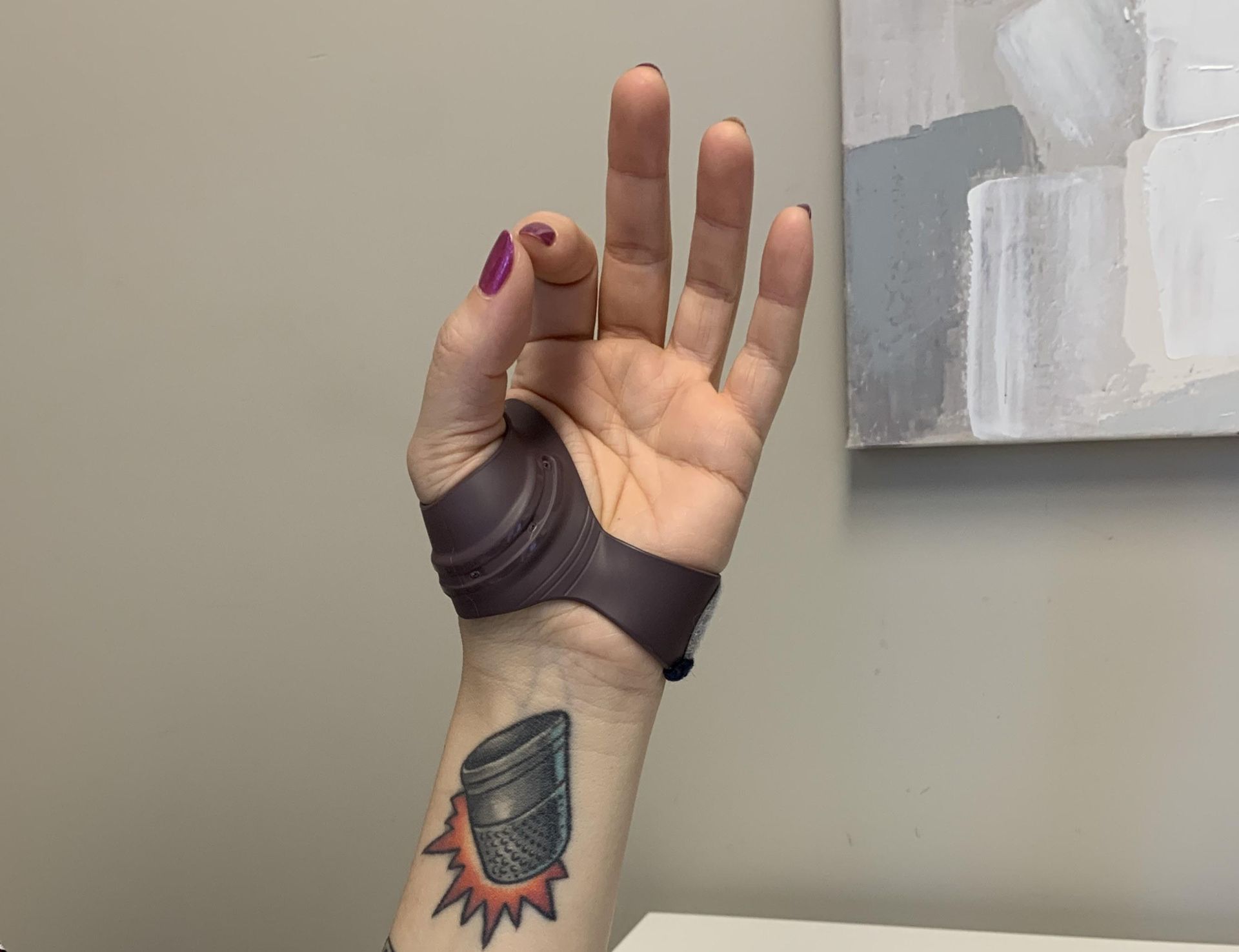
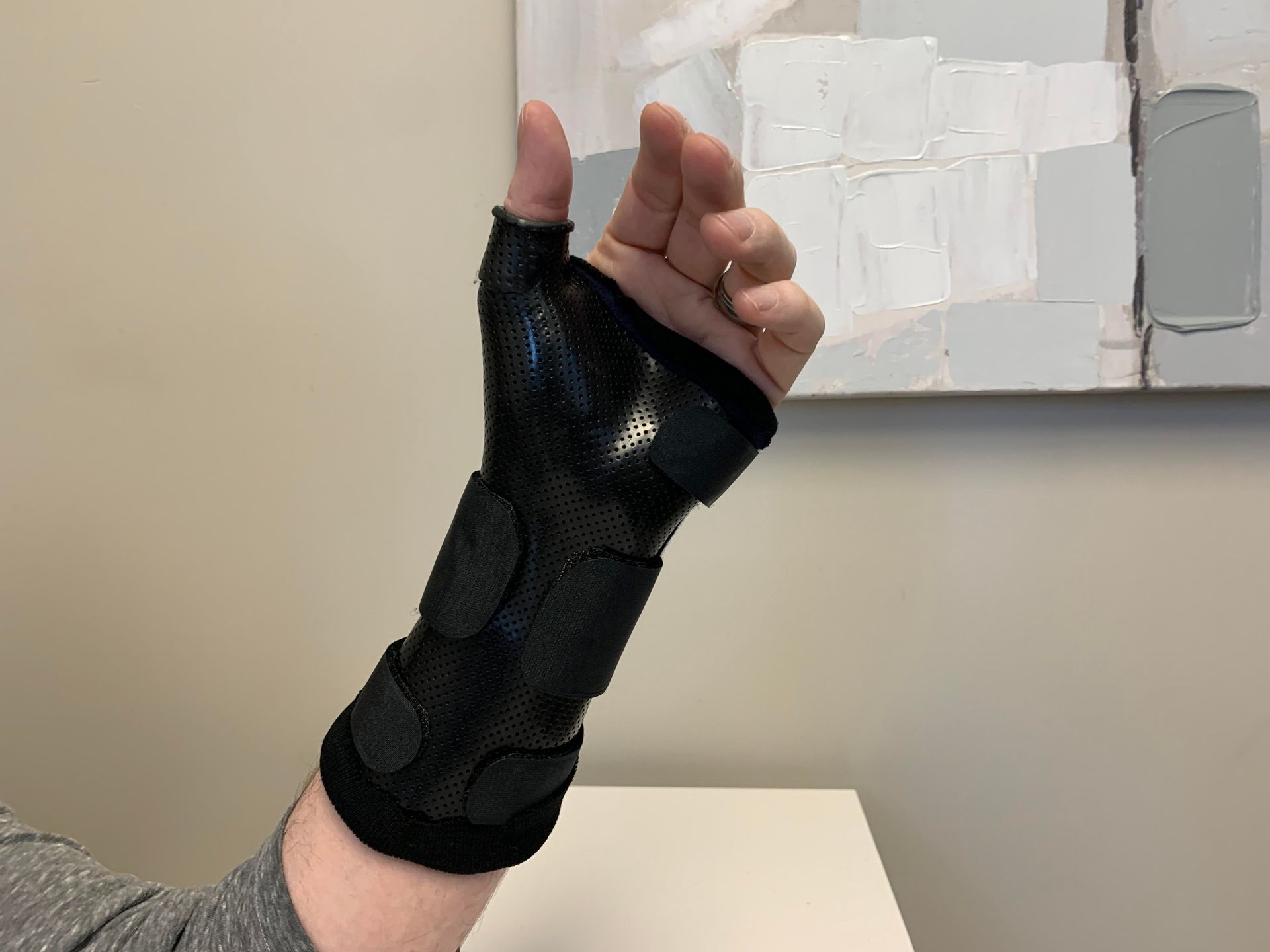
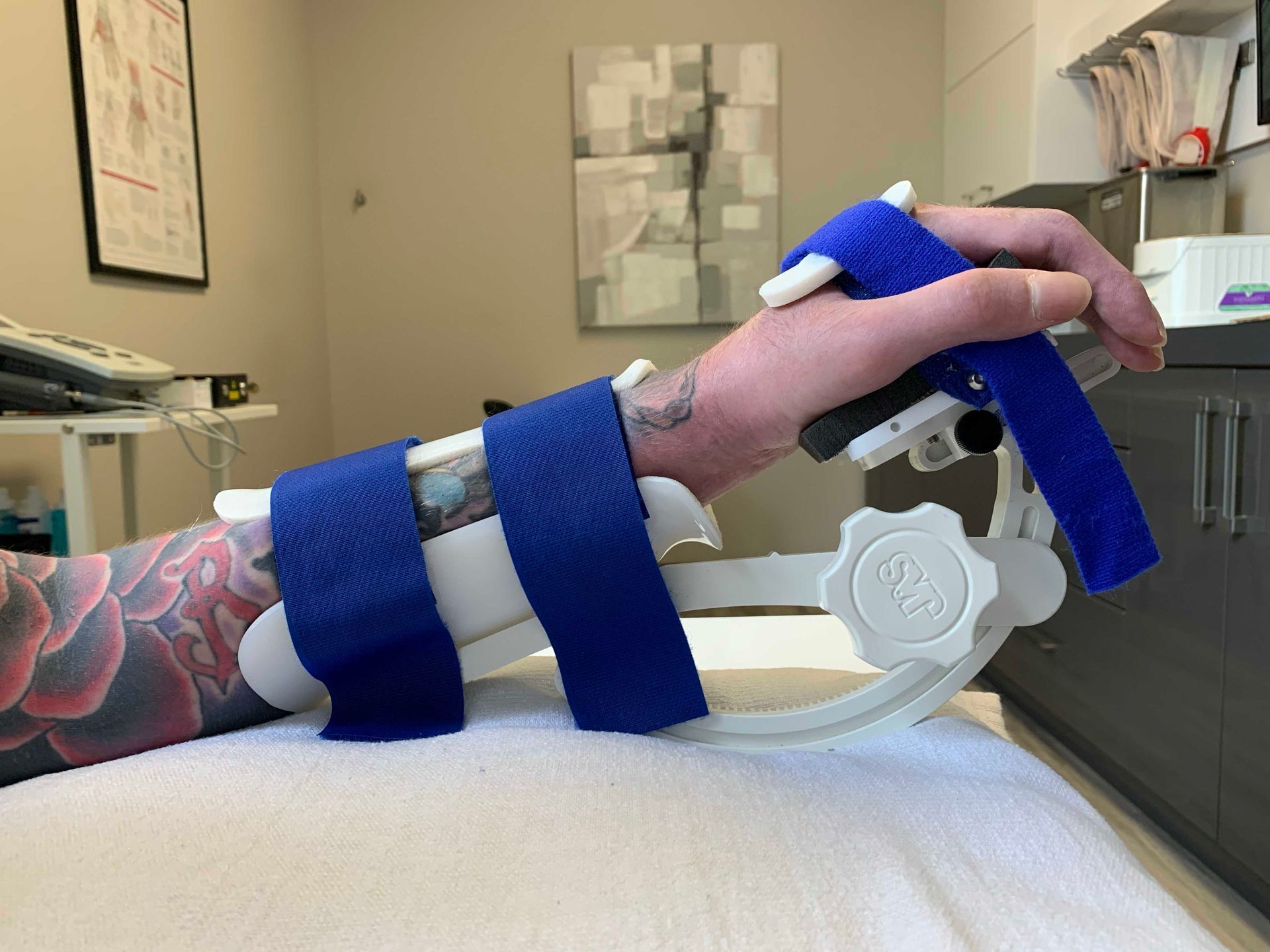
Splinting and Bracing
Individually, or as a component of a hand therapy treatment program, splints can be essential in assisting hand and upper extremity injured clients make a successful recovery. Splints may be used to protect healing structures, prevent deformity or to help stretch or strengthen injured structures. Splints may be custom fabricated or may be prefabricated. Custom splints are made with low temperature thermoplastic and are fabricated on site. Most extended health care insurance plans cover the fabrication and/or provision of splints.


Ergonomic Assessment
The Hand Clinic provides clients with ergonomic assessments which are conducted in their workplace or home to facilitate improved outcomes following traumatic or work-related injuries. The cost of ergonomic assessments may often be covered by employers to prevent future worker injuries. Our goal is to recommend sensible and cost-effective ergonomic solutions for our clients and their employers.
What is Ergonomics?
Ergonomics is the study of how workspace and job design affect worker health and wellbeing. It includes factors such as physical workspace design, adjustability, job design (time and length of breaks, variety of tasks, and pace of work), as well as individual work style.
Why is Practising Good Ergonomics Important?
The way you work affects your well-being. Many aches and pains associated with work are avoidable with a few simple adjustments. The goal of an ergonomic assessment is to provide education and resources to reduce the risk of musculoskeletal disorders and to maintain a healthy workforce.
Benefits for Employers
- Reduced worker absenteeism
- Reduced worker turnover rate
- Increased worker productivity
- Reduced number of worker accidents
Benefits for Employees
- Improved comfort at work
- Increased energy levels
- Faster recovery from accident or disease
- Improved job and life satisfaction
- Improved overall health
What Does an Ergonomic Assessment Consist of?
- Client interview
- Assessment of the client, his or her tasks and the work area
- Instruction of how to properly set up and operate current workstation equipment
- Provision of an ergonomic assessment report outlining identified ergonomic risk factors and recommendations including specific equipment
- Follow-up visit to assist in equipment set up to ensure new equipment is achieving desired ergonomic goals





